India has entered a turning point in its labour landscape. For decades, employers faced 29 confusing laws. These rules slowed compliance and discouraged investment. As a result, India fell behind emerging manufacturing hubs like Vietnam and Bangladesh.
That era is over.
India will move from scattered rules to a unified structure. The four new labor codes will take effect on November 21, 2025. This change isn’t just about admin tasks. It’s a total redesign of how organizations hire, manage, protect, and pay their workers.
The reform balances two imperatives India has struggled to align for years:
Protect workers with stronger rights. Give employers the flexibility needed to stay competitive.
And when a reform manages to do both, it becomes foundational – not temporary.
Understanding the Four Labour Codes: The Backbone of the Reform
1. Code on Wages, 2019 – One Definition, One Framework
The new wage code solves an old issue: India had too many ways to define “wages.” Different laws defined terms differently. This caused disputes in calculating gratuity, PF, and bonuses.
The new code gives India a single, universal definition of wages.
What this changes for employers:
- Minimum wages are now standardized nationwide.
- The “floor wage” sets a unified base rate across sectors.
- All statutory benefits draw from the same wage definition.
- Ambiguities that created litigation risk are removed.
This gives organizations predictable cost structures and workers transparent benefit calculations.
2. Code on Social Security, 2020 – Expanding Protection Beyond Traditional Jobs
India’s workforce has evolved faster than its laws. Gig workers, delivery partners, independent drivers, and platform earners missed out on the old rules.
The new Social Security Code fixes this gap.
Key shifts:
- Social protection now extends to gig workers, platform workers, and the unorganized sector.
- Platform aggregators must give 1–2% of their annual turnover. This is capped at 5% of what they pay gig workers, and it goes to social welfare funds.
- Life insurance, disability cover, health support, maternity benefits, and retirement protection are all part of the plan.
India now recognizes non-traditional work as key to its economy and offers protection for it.
3. Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020 – Modern Standards for Modern Workplaces
This code updates India’s workplace safety rules. It aligns them with today’s risks instead of old factory-era standards.
What the new standards ensure:
- Clear rules on working hours, leave entitlements, overtime, and health measures.
- Night shift permissions for women with mandatory safety protocols.
- Stricter, enforceable safety requirements across industries.
- Uniform rules for establishments employing workers in varied environments.
The compliance expectation is higher. So is the accountability.
4. Industrial Relations Code, 2020 – Stability and Flexibility in the Same Framework
India’s past industrial laws defined any establishment with over 100 workers as a large enterprise. The result was less flexibility in the workforce, delays in restructuring, and slower responses to market changes.
The new code updates this.
Key shift: Organizations must now get government approval for layoffs or retrenchments only if they have over 300 workers, not 100.
This helps businesses be more agile. It also keeps workers protected with notice periods and compensation plans.
Employee vs Worker Classification: Why This Distinction Matters Now
The new codes draw a clear boundary between:
- Workers (manual, operational, technical, clerical roles)
- Employees (supervisory, managerial, administrative roles)
This distinction affects:
- Eligibility for overtime
- Leave encashment
- Standing orders
- Safety protections
- Working hour rules
- Disciplinary procedures
Organizations should classify roles based on what each person actually does, not their job title. This area will face close scrutiny for misclassification risk, especially in audits.
Unified Definition of Wages: Clarity, Stability, and Cost Impact
The new wage definition applies across:
- PF
- Bonus
- Gratuity
- Leave encashment
- Overtime
- ESIC
- Retrenchment compensation
Impact on employers: More salary components fall within “wages,” increasing statutory benefit payouts. Certain allowances may no longer be used to reduce statutory liabilities. Variable and incentive-linked parts can still lead to confusion. This means we might need to redesign compensation in a structured way.
This is where organizations must align HR, payroll, and compliance teams.
Contract Labour & Fixed-Term Employment: Structured Flexibility
Restrictions on Contract Labour in Core Activities
Contract workers can’t work in core operations unless there are specific exceptions.
This forces organizations to:
- Clearly define what core is and what is ancillary
- Maintain documentation justifying contract deployment
- Reassess staffing structures across business units
This change aims to stop unfair labor substitution. It won’t block genuine business needs.
Fixed-Term Employment Gets Full Legal Recognition
FTE is finally formalized.
What changes:
- Fixed-term workers receive benefits at par with permanent workers.
- Gratuity eligibility begins at 1 year, not 5.
- No wage discrimination compared to permanent employees in similar roles.
This makes FTE a reliable alternative to contract labour while maintaining fairness for workers.
Flexible Work Hours and 4-Day Work Week Options
The central code grants states the authority to establish specific working-hour rules.
Some states- including Haryana and Odisha – have already moved toward:
- 4-day work weeks
- 12-hour daily shifts (with required rest periods)
- More flexible weekly scheduling structures
Organizations must track both:
- Central Labour Code Requirements
- Individual state Shops & Establishments rules
This dual compliance landscape means HR teams must run state-specific policy handbooks.
Gig and Platform Worker Social Security – India’s Most Forward-Looking Reform
The codes formally acknowledge gig workers as part of India’s economic engine.
Platform aggregator obligations:
- Contribute 1–2% of annual turnover
- Cap set at 5% of gig worker payouts
- Mandatory enrollment in notified welfare schemes
This reform directly impacts e-commerce, mobility tech, logistics, hyperlocal delivery, and freelance marketplaces. It establishes a strong foundation for lasting protection in a segment that previously had no safety net.
Layoffs, Retrenchment & Re-Skilling Fund – Balanced Flexibility
Higher Threshold for Approval
Only establishments with 300 or more workers now require government approval to downsize.
Re-Skilling Support for Workers
Employers must pay 15 days of the last drawn wages for each retrenched worker into a re-skilling fund.
This gives flexibility to organizations while ensuring displaced workers receive transitional support.
Women’s Night Shift Provisions – Opportunity with Responsibility
Women can now work night shifts if employers provide:
- Safe transportation
- Proper supervision
- Security protocols
- Emergency support
This gives access to industries that were hard to reach. It also makes employers clearly accountable for safety.
Mandatory Appointment Letters – Ending Informal Employment
All employees must now receive formal appointment letters outlining:
- Role and responsibilities
- Working hours
- Compensation
- Leave
- Benefits
- Terms and conditions
This improves transparency and reduces disputes. Organizations need to update their hiring processes to remain competitive. This ensures compliance for all types of employees and workers.
Strategic Compliance Roadmap for Organizations
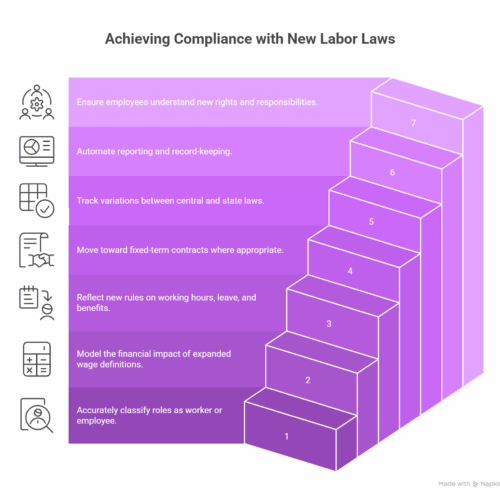
1. Reassess job roles and classifications
Accurately map roles to “worker” or “employee” categories.
2. Review salary structures
Model the financial impact of expanded wage definitions.
3. Rebuild HR and payroll policies
Reflect new rules on working hours, leave, overtime, and benefits.
4. Redesign hiring models
Move toward fixed-term contracts where appropriate.
5. Build a state-specific compliance matrix
Track variations between central codes and state Shops & Establishments Acts.
6. Implement digital compliance systems
Automate reporting, records, filings, and document trails.
7. Train your workforce
Employees must understand new rights, benefits, and responsibilities.
Why These Codes Matter
Strengthening India’s Competitiveness
Unified labor laws make compliance easier, cut regulatory friction, and boost India’s appeal for global investors looking at Asian manufacturing options.
Raising Worker Protection Standards
Both formal and gig workers get stronger safety nets, predictable wages, and structured benefits.
Driving India’s Employment Modernization
India meets global labor standards by using digital tools, keeping formal documents, ensuring flexible structures, and updating safety rules.
Conclusion
The 2025 labour codes do more than update laws. They change how Indian employment will function for the next ten years.
Organizations that approach compliance proactively will benefit from:
- Predictable cost structures
- Reduced litigation risk
- Stronger employer branding
- Better workforce stability
- Improved operational flexibility
Those who delay will face compliance gaps, penalties, and workforce dissatisfaction.
A structured compliance roadmap isn’t optional anymore. It’s key to risk management and business planning.
